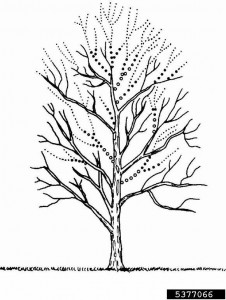
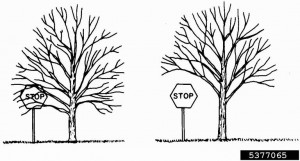
In the process of pruning trees, master the correct pruning method, and through reasonable pruning, you can cultivate a beautiful tree shape. The pruning of trees further regulates the rational distribution of nutrients, inhibits overgrowth, promotes the differentiation of flower buds, achieves early flowering and fruiting of young trees, prolongs the blooming and fruiting periods, and can also rejuvenate old trees. There are three main methods of pruning garden trees, which can be summarized as Crown Reduction, Crown Thinning, and Crown Raising.
1. Crown Reduction, Its main purpose is to stimulate the germination of side buds, draw new shoots, increase the number of branches, and produce more leaves and more flowers. According to the degree of cut, it can be divided into the following types:
1. Light cut: lightly cut the top tips of branches (cut off 1/5-1/4 of the full length of the branches), mainly used for pruning strong branches of flowering and fruit trees. This pruning method stimulates the germination of most semi-full buds in the lower part of the branches after removing the top tips, disperses the nutrients of the branches so that the branches of the garden ornamental flowers and fruit trees in the coming year can produce more medium and short branches, which are easy to form flower buds.
2. Medium cut: cut to the middle or middle-upper part of the branches with full buds (the length of the cut branches is 1/3-1/2), which is mainly used for the rejuvenation of some weak branches and the cultivation of backbone branches and extended branches of various trees.
3. Heavy short cut: cut off 2/3-3/4 of the full length of the branches. This pruning method has a greatly stimulating effect and is mainly used for the regeneration and rejuvenation of weak trees, old trees, and old weak branches.
4. Extremely heavy cut: Leave 1-2 deflated buds at the base of the tree, and cut off the rest. Lagerstroemia in the garden often uses this method.
5. Retraction: cut off part of the perennial branches. Because the trees have grown for many years and are far from the top of the branches, the base is easy to bear legs. In order to reduce the top position and promote the regeneration of the base of the perennial branches, retractive pruning methods are often used.
Second, Crown Thinning. Cut the branches from the meristem, thinning can adjust the even distribution of the branches, increase the space, improve the ventilation and light conditions, which is conducive to the growth and development of the branches in the crown and the differentiation of flower buds. The objects of thinning are mainly diseased and insect branches, dry and dead branches, and overly dense cross branches.
3. Crown Raising: remove the twigs or root tillers that grew out of the roots at the base of the tree trunk and near the wound. Avoid these branches and root tillers, which will hinder the shape of the tree and disperse the nutrients of the tree.
Matters needing attention during tree pruning:
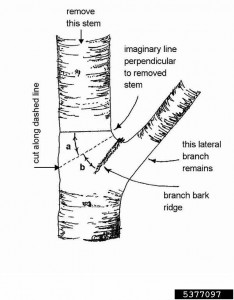
1. The cutting mouth of the pruning branches should be smooth, and the inclined plane with a 45-degree angle to the cutting mouth bud, cut down from the opposite side of the cutting mouth, the upper part of the inclined plane is level with the cutting mouth bud tip, and the lowest part of the inclined plane is level with the bud base. The cut wound is small, easy to heal, and the bud grows quickly after germination. Cut the cut of the thin branch at the branch point, and it is level with the stem, leaving no residual pile. The sparse branches of bushy shrubs are level with the ground.
The direction and quality of the cut buds determine the growth direction of the new shoots and the growth direction of the branches. The direction of cutting sprouts should be considered from the distribution of the branches in the crown and the strength of the expected growth of new branches. When the crown needs to be expanded outwards, the cutting sprouts should stay outside of the branches. Inward, for the overgrown branches, in order to suppress the growth of the branches, use the weak buds as the cut buds, and choose the full and strong buds when supporting the weak branches.
2. The pruning period of deciduous trees and evergreen trees should be different. In winter, deciduous trees stop growing. At this time, pruning loses fewer nutrients and wounds heal faster. Although evergreen trees are dormant in winter, there is a danger of freezing damage if the branches and leaves are cut off. Since the roots, branches, and leaves of evergreen trees are active throughout the year, the metabolism is not stopped, so the nutrients in the leaves are not completely used for storage. When the branches and leaves are cut, the nutrients are lost, which affects the growth of the trees. The pruning period of evergreen trees is generally in late spring after winter.